En este post vamos a ver como automatizar la caída de servicio y de un servidor alojado en vmware mediante ansible AWX, para ello antes vamos a crear una nueva tarea
Debemos crear dos jobs, uno para reiniciar el servicio si este se encuentra caído y otro el cual comprueba si la maquina en vmware responde mediante las vmware tools y en caso de que no responda la reinicia, Para la creación de estos jobs vamos a utilizar el siguiente proyecto: https://gitlab.com/rokitoh/automatizaciones_nagios/
Es necesario configurar todas las variables en el fichero vars.yml para que pueda realizar la conexión contra el vcenter y el servidor Windows.
También tenemos que modificar el archivo maquina.yml el texto DATACENTER-VMWARE por el nombre de nuestro datacenter en vmware
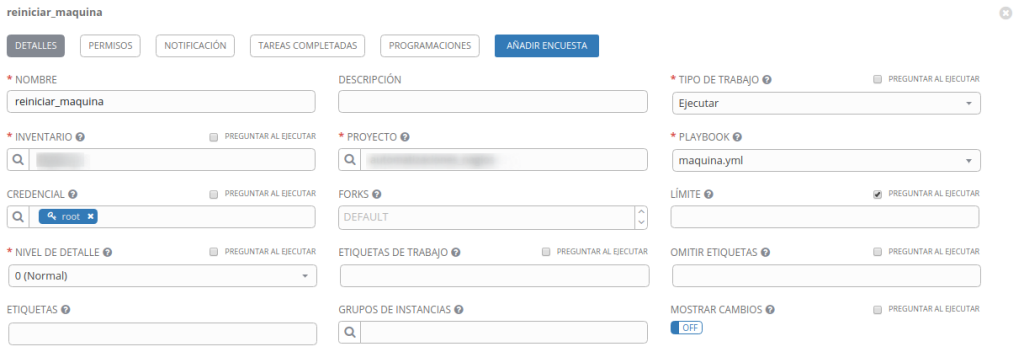
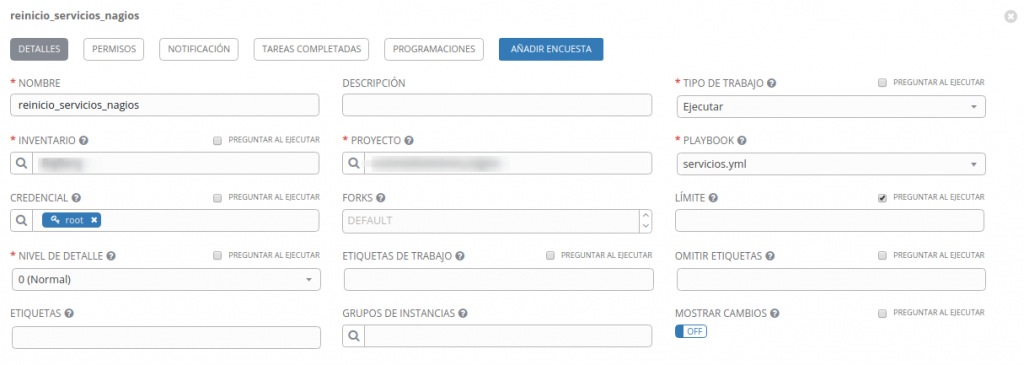
Instalamos el paquete ansible-tower-cli mediante pip
pip install ansible-tower-cliUna vez instalado debemos configurar la conexión hacia nuestro Ansible AWX, par ello ejecutamos los siguientes comandos
tower-cli config host http://192.168.1.111
tower-cli config username nagios
tower-cli config password nagiospasswod
tower-cli config verify_ssl falseListamos todos los job para ver que identificador tienen nuestras tareas creadas anteriormente en Ansible AWX, como podemos ver en mi caso son el 48 reinicio de servicios y 49 reinicio de servidor.
tower-cli job_template list
== ======================================= ========= ======= =========================
id name inventory project playbook
== ======================================= ========= ======= =========================
49 reiniciar_maquina 2 47 maquina.yml
48 reinicio_servicios_nagios 2 47 servicios.yml
Tras identificar los jobs debemos agregar en /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/eventhandlers.cfg el siguiente texto (teniendo en cuenta que debemos modificar el ID del parámetro –template )
define command {
command_name servicio_ansible
command_line python /usr/bin/tower_handler.py --state '$SERVICESTATE$' --attempt '$SERVICEATTEMPT$' --downtime '$SERVICEDOWNTIME$' --host_downtime '$HOSTDOWNTIME$' --service '$SERVICEDESC$' --hostname '$HOSTADDRESS$' --template 48 --inventory '$ARG1$' --extra_vars '$ARG2$' --limit '$ARG3$'
}
define command {
command_name host_ansible
command_line python /usr/bin/tower_handler.py --state '$SERVICESTATE$' --attempt '$SERVICEATTEMPT$' --downtime '$SERVICEDOWNTIME$' --host_downtime '$HOSTDOWNTIME$' --service '$SERVICEDESC$' --hostname '$HOSTADDRESS$' --template 49 --inventory '$ARG1$' --limit '$ARG2$'
}
Ahora debemos agregar la siguiente linea en el fichero /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/eventhandlers.cfgDescargamos y copiamos el plugin en la ruta
wget https://github.com/ansible/tower-nagios-integration/blob/master/tower_handler.py
cp tower_handler.py /usr/bin/Ahora si queremos agregar en un servicio para que cuando identifique que este caído lo levante automáticamente debemos definirlo mediante un event handler
event_handler servicio_ansible!<INVENTARIO ANSIBLE>!servicio: <NOMBRE DEL SERVICIO>!<SERVIDOR>*Ejemplo:
define service {
use redorbia-serv
host_name redorbitaweb
service_description Servicio - MySQL
check_command check_process_snmp_stats!redorbita!mysqld!0,3!0
event_handler servicio_ansible!inventoryredorbita!servicio: mariadb!redorbitaweb*
}
De la misma forma debemos definir el host
define host {
use redorbia-host
host_name redorbitaweb
alias redorbitaweb
address 192.168.1.111
event_handler host_ansible!inventoryredorbita!redorbitaweb*
}:wq!