¿Que es FreeIPA?
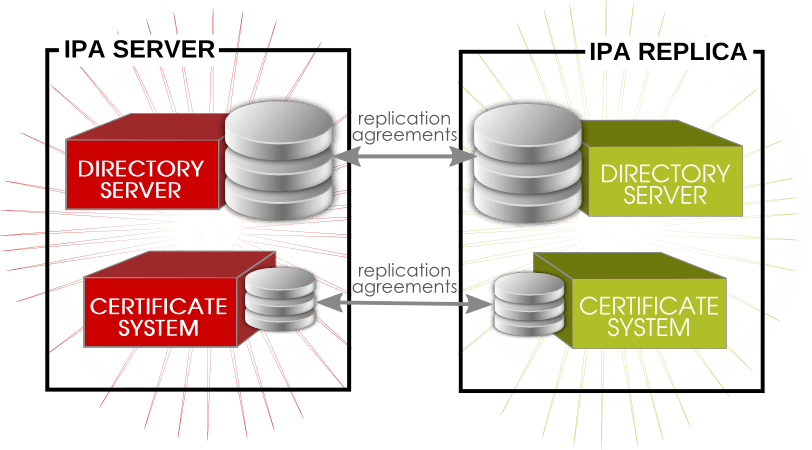 FreeIPA, es un proyecto de suite de software de código fuente libre mantenida por el Proyecto Fedora, patrocinada por RedHat, el nombre significa Identidad|Políticas|Auditoría Libre (en inglés, Free Identity|Policy|Audit), tiene por objetivo proveer un interfaz segura y sencilla para la administración de identidades comparable a Novell Identity Manager, IBM Security Directory Suite, Redhat 389 Directory Server, Apache Directory Studio y Microsoft Active Directory, orientado principalmente en entornos de red basados en GNU/Linux y entornos posix compatible.
FreeIPA, es un proyecto de suite de software de código fuente libre mantenida por el Proyecto Fedora, patrocinada por RedHat, el nombre significa Identidad|Políticas|Auditoría Libre (en inglés, Free Identity|Policy|Audit), tiene por objetivo proveer un interfaz segura y sencilla para la administración de identidades comparable a Novell Identity Manager, IBM Security Directory Suite, Redhat 389 Directory Server, Apache Directory Studio y Microsoft Active Directory, orientado principalmente en entornos de red basados en GNU/Linux y entornos posix compatible.
Lanzada oficialmente en 2008, el proyecto en sí mismo refiere a una herramienta de instalación y un entorno de administración de servicios e identidades, basado en el proyecto 389 Directory Server de RedHat, e integra a múltiples proyectos preexistentes como1 : OpenLDAP para el servicio de directorio, MIT Kerberos 5 para la autenticación y sesiones, Apache HTTP Server y Apache Tomcat para la interfaz de administración y web service, Python principalmente para las herramientas de instalación y configuración de sistema, NTP para sincronización de horaria, Dogtag para la integración de certificados CA y RA y un plugin personalizado de BIND para gestionar los DNS; desde la versión 3.x incluye gestión de Samba la integración con Microsoft Active Directory mediante Cross Forest Trusts (bosques cruzados confiables). El mayor acierto del proyecto es proveer una interfaz web de administración de identidades y la administración de los servicios integrados.
Inicialmente el proyecto soportaba como servidor Fedora 19, posteriormente RedHat, Centos, OpenSuSE2 , Debian compatibles3 4 . Además de soportar los clientes las distribuciones basadas en RedHat, y otras distribuciones5 y sistemas posix, posee soporte sistemas Microsoft Windows y Apple MacOS X.
Este leboratorio contara con dos servidores:
Dominio: redorbita.com
freeipa01 Master – 192.168.1.80/24
freeipa02 Replica – 192.168.1.81/24
Configuración /etc/hosts
Añadimos en ambos servidores (freeipa01 y freeipa02) el FQDN para que puedan resolver correctamente mediante nombre.
192.168.1.80 freeipa01.redorbita.com freeipa01
192.168.1.81 freeipa02.redorbita.com freeipa02
Procedemos a empezar la instalación del servidor master (freeipa01)
Instalamos los paquetes necesarios:
yum install -y ipa-server bind bind-dyndb-ldap ipa-server-dns
Ejecutamos el script de instalación
[root@freeipa01 ~]# ipa-server-install
The log file for this installation can be found in /var/log/ipaserver-install.log
==============================================================================
This program will set up the IPA Server.This includes:
* Configure a stand-alone CA (dogtag) for certificate management
* Configure the Network Time Daemon (ntpd)
* Create and configure an instance of Directory Server
* Create and configure a Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC)
* Configure Apache (httpd)To accept the default shown in brackets, press the Enter key.
Do you want to configure integrated DNS (BIND)? [no]: yes
Enter the fully qualified domain name of the computer
on which you’re setting up server software. Using the form
<hostname>.<domainname>
Example: master.example.com.Server host name [freeipa01.redorbita.com]:
Warning: skipping DNS resolution of host freeipa01.redorbita.com
The domain name has been determined based on the host name.Please confirm the domain name [redorbita.com]:
The kerberos protocol requires a Realm name to be defined.
This is typically the domain name converted to uppercase.Please provide a realm name [REDORBITA.COM]:
Certain directory server operations require an administrative user.
This user is referred to as the Directory Manager and has full access
to the Directory for system management tasks and will be added to the
instance of directory server created for IPA.
The password must be at least 8 characters long.Directory Manager password:
Password (confirm):The IPA server requires an administrative user, named ‘admin’.
This user is a regular system account used for IPA server administration.IPA admin password:
Password (confirm):Existing BIND configuration detected, overwrite? [no]: yes
Do you want to configure DNS forwarders? [yes]: yes
Enter an IP address for a DNS forwarder, or press Enter to skip:
No DNS forwarders configured
Do you want to configure the reverse zone? [yes]: yes
Please specify the reverse zone name [1.168.192.in-addr.arpa.]:
Using reverse zone(s) 1.168.192.in-addr.arpa.The IPA Master Server will be configured with:
Hostname: freeipa01.redorbita.com
IP address(es): 192.168.1.80
Domain name: redorbita.com
Realm name: REDORBITA.COMBIND DNS server will be configured to serve IPA domain with:
Forwarders: No forwarders
Reverse zone(s): 1.168.192.in-addr.arpa.Continue to configure the system with these values? [no]: yes
The following operations may take some minutes to complete.
Please wait until the prompt is returned.Configuring NTP daemon (ntpd)
[1/4]: stopping ntpd
[2/4]: writing configuration
[3/4]: configuring ntpd to start on boot
[4/4]: starting ntpd
Done configuring NTP daemon (ntpd).
Configuring directory server (dirsrv). Estimated time: 1 minute
[1/42]: creating directory server user
[2/42]: creating directory server instance
[3/42]: adding default schema
[4/42]: enabling memberof plugin
[5/42]: enabling winsync plugin
[6/42]: configuring replication version plugin
[7/42]: enabling IPA enrollment plugin
[8/42]: enabling ldapi
[9/42]: configuring uniqueness plugin
[10/42]: configuring uuid plugin
[11/42]: configuring modrdn plugin
[12/42]: configuring DNS plugin
[13/42]: enabling entryUSN plugin
[14/42]: configuring lockout plugin
[15/42]: creating indices
[16/42]: enabling referential integrity plugin
[17/42]: configuring certmap.conf
[18/42]: configure autobind for root
[19/42]: configure new location for managed entries
[20/42]: configure dirsrv ccache
[21/42]: enable SASL mapping fallback
[22/42]: restarting directory server
[23/42]: adding default layout
[24/42]: adding delegation layout
[25/42]: creating container for managed entries
[26/42]: configuring user private groups
[27/42]: configuring netgroups from hostgroups
[28/42]: creating default Sudo bind user
[29/42]: creating default Auto Member layout
[30/42]: adding range check plugin
[31/42]: creating default HBAC rule allow_all
[32/42]: adding entries for topology management
[33/42]: initializing group membership
[34/42]: adding master entry
[35/42]: initializing domain level
[36/42]: configuring Posix uid/gid generation
[37/42]: adding replication acis
[38/42]: enabling compatibility plugin
[39/42]: activating sidgen plugin
[40/42]: activating extdom plugin
[41/42]: tuning directory server
[42/42]: configuring directory to start on boot
Done configuring directory server (dirsrv).
Configuring certificate server (pki-tomcatd). Estimated time: 3 minutes 30 seconds
[1/28]: creating certificate server user
[2/28]: configuring certificate server instance
[3/28]: stopping certificate server instance to update CS.cfg
[4/28]: backing up CS.cfg
[5/28]: disabling nonces
[6/28]: set up CRL publishing
[7/28]: enable PKIX certificate path discovery and validation
[8/28]: starting certificate server instance
[9/28]: creating RA agent certificate database
[10/28]: importing CA chain to RA certificate database
[11/28]: fixing RA database permissions
[12/28]: setting up signing cert profile
[13/28]: setting audit signing renewal to 2 years
[14/28]: restarting certificate server
[15/28]: requesting RA certificate from CA
[16/28]: issuing RA agent certificate
[17/28]: adding RA agent as a trusted user
[18/28]: authorizing RA to modify profiles
[19/28]: configure certmonger for renewals
[20/28]: configure certificate renewals
[21/28]: configure RA certificate renewal
[22/28]: configure Server-Cert certificate renewal
[23/28]: Configure HTTP to proxy connections
[24/28]: restarting certificate server
[25/28]: migrating certificate profiles to LDAP
[26/28]: importing IPA certificate profiles
[27/28]: adding default CA ACL
[28/28]: updating IPA configuration
Done configuring certificate server (pki-tomcatd).
Configuring directory server (dirsrv). Estimated time: 10 seconds
[1/3]: configuring ssl for ds instance
[2/3]: restarting directory server
[3/3]: adding CA certificate entry
Done configuring directory server (dirsrv).
Configuring Kerberos KDC (krb5kdc). Estimated time: 30 seconds
[1/10]: adding sasl mappings to the directory
[2/10]: adding kerberos container to the directory
[3/10]: configuring KDC
[4/10]: initialize kerberos container
WARNING: Your system is running out of entropy, you may experience long delays
[5/10]: adding default ACIs
[6/10]: creating a keytab for the directory
[7/10]: creating a keytab for the machine
[8/10]: adding the password extension to the directory
[9/10]: starting the KDC
[10/10]: configuring KDC to start on boot
Done configuring Kerberos KDC (krb5kdc).
Configuring kadmin
[1/2]: starting kadmin
[2/2]: configuring kadmin to start on boot
Done configuring kadmin.
Configuring ipa_memcached
[1/2]: starting ipa_memcached
[2/2]: configuring ipa_memcached to start on boot
Done configuring ipa_memcached.
Configuring ipa-otpd
[1/2]: starting ipa-otpd
[2/2]: configuring ipa-otpd to start on boot
Done configuring ipa-otpd.
Configuring the web interface (httpd). Estimated time: 1 minute
[1/19]: setting mod_nss port to 443
[2/19]: setting mod_nss protocol list to TLSv1.0 – TLSv1.2
[3/19]: setting mod_nss password file
[4/19]: enabling mod_nss renegotiate
[5/19]: adding URL rewriting rules
[6/19]: configuring httpd
[7/19]: configure certmonger for renewals
[8/19]: setting up ssl
[9/19]: importing CA certificates from LDAP
[10/19]: setting up browser autoconfig
[11/19]: publish CA cert
[12/19]: creating a keytab for httpd
[13/19]: clean up any existing httpd ccache
[14/19]: configuring SELinux for httpd
[15/19]: create KDC proxy user
[16/19]: create KDC proxy config
[17/19]: enable KDC proxy
[18/19]: restarting httpd
[19/19]: configuring httpd to start on boot
Done configuring the web interface (httpd).
Applying LDAP updates
Upgrading IPA:
[1/9]: stopping directory server
[2/9]: saving configuration
[3/9]: disabling listeners
[4/9]: enabling DS global lock
[5/9]: starting directory server
[6/9]: upgrading server
[7/9]: stopping directory server
[8/9]: restoring configuration
[9/9]: starting directory server
Done.
Restarting the directory server
Restarting the KDC
Configuring DNS (named)
[1/12]: generating rndc key file
WARNING: Your system is running out of entropy, you may experience long delays
[2/12]: adding DNS container
[3/12]: setting up our zone
[4/12]: setting up reverse zone
[5/12]: setting up our own record
[6/12]: setting up records for other masters
[7/12]: adding NS record to the zones
[8/12]: setting up CA record
[9/12]: setting up kerberos principal
[10/12]: setting up named.conf
[11/12]: configuring named to start on boot
[12/12]: changing resolv.conf to point to ourselves
Done configuring DNS (named).
Configuring DNS key synchronization service (ipa-dnskeysyncd)
[1/7]: checking status
[2/7]: setting up bind-dyndb-ldap working directory
[3/7]: setting up kerberos principal
[4/7]: setting up SoftHSM
[5/7]: adding DNSSEC containers
[6/7]: creating replica keys
[7/7]: configuring ipa-dnskeysyncd to start on boot
Done configuring DNS key synchronization service (ipa-dnskeysyncd).
Restarting ipa-dnskeysyncd
Restarting named
Restarting the web server
==============================================================================
Setup completeNext steps:
1. You must make sure these network ports are open:
TCP Ports:
* 80, 443: HTTP/HTTPS
* 389, 636: LDAP/LDAPS
* 88, 464: kerberos
* 53: bind
UDP Ports:
* 88, 464: kerberos
* 53: bind
* 123: ntp2. You can now obtain a kerberos ticket using the command: ‘kinit admin’
This ticket will allow you to use the IPA tools (e.g., ipa user-add)
and the web user interface.Be sure to back up the CA certificates stored in /root/cacert.p12
These files are required to create replicas. The password for these
files is the Directory Manager password
Configuramos las reglas en el firewall en ambos servidores (freeipa01 y freeipa02).
[root@freeipa01 ~]# firewall-cmd –permanent –add-service={ntp,http,https,ldap,ldaps,kerberos,kpasswd,dns}
success
[root@freeipa01 ~]# firewall-cmd –reload
success
Ahora vamos a proceder a configurar la replica.
Instalamos los paquetes necesarios
yum install -y ipa-server bind bind-utils bind-dyndb-ldap ipa-server-dns
Nos logamos como admin en freeipa01
[root@freeipa01 ~]# kinit admin
Password for admin@REDORBITA.COM:
Creamos un registro tipo A (host) en el DNS:
[root@freeipa01 ~]# ipa dnsrecord-add redorbita.com freeipa02 –a-rec 192.168.1.81
Nombre de registro: freeipa02
A registro: 192.168.1.81
Creamos la zona inversa
[root@freeipa01 ~]# ipa dnsrecord-add 1.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 81 –ptr-rec freeipa02.redorbita.com.
Nombre de registro: 81
PTR registro: freeipa02.redorbita.com.
Establecemos la replica
[root@freeipa01 ~]# ipa-replica-prepare freeipa02.redorbita.com
Directory Manager (existing master) password:Preparing replica for freeipa02.redorbita.com from freeipa01.redorbita.com
Creating SSL certificate for the Directory Server
Creating SSL certificate for the dogtag Directory Server
Saving dogtag Directory Server port
Creating SSL certificate for the Web Server
Exporting RA certificate
Copying additional files
Finalizing configuration
Packaging replica information into /var/lib/ipa/replica-info-freeipa02.redorbita.com.gpg
The ipa-replica-prepare command was successful
Transferimos la clave creada de freeipa01 a freeipa02
scp /var/lib/ipa/replica-info-freeipa02.redorbita.com.gpg root@freeipa02.redorbita.com:/var/lib/ipa
Promocionamos freeipa02 como replica:
[root@freeipa02 ~]# ipa-replica-install –setup-dns –setup-ca –no-forwarders /var/lib/ipa/replica-info-freeipa02.redorbita.com.gpg
Directory Manager (existing master) password:Existing BIND configuration detected, overwrite? [no]: yes
Using reverse zone(s) 1.168.192.in-addr.arpa.
Run connection check to master
Check connection from replica to remote master ‘freeipa01.redorbita.com’:
Directory Service: Unsecure port (389): OK
Directory Service: Secure port (636): OK
Kerberos KDC: TCP (88): OK
Kerberos Kpasswd: TCP (464): OK
HTTP Server: Unsecure port (80): OK
HTTP Server: Secure port (443): OKThe following list of ports use UDP protocol and would need to be
checked manually:
Kerberos KDC: UDP (88): SKIPPED
Kerberos Kpasswd: UDP (464): SKIPPEDConnection from replica to master is OK.
Start listening on required ports for remote master check
Get credentials to log in to remote master
admin@REDORBITA.COM password:Check SSH connection to remote master
Execute check on remote master
Check connection from master to remote replica ‘freeipa02.redorbita.com’:
Directory Service: Unsecure port (389): OK
Directory Service: Secure port (636): OK
Kerberos KDC: TCP (88): OK
Kerberos KDC: UDP (88): OK
Kerberos Kpasswd: TCP (464): OK
Kerberos Kpasswd: UDP (464): OK
HTTP Server: Unsecure port (80): OK
HTTP Server: Secure port (443): OKConnection from master to replica is OK.
Connection check OK
Configuring NTP daemon (ntpd)
[1/4]: stopping ntpd
[2/4]: writing configuration
[3/4]: configuring ntpd to start on boot
[4/4]: starting ntpd
Done configuring NTP daemon (ntpd).
Configuring directory server (dirsrv). Estimated time: 1 minute
[1/38]: creating directory server user
[2/38]: creating directory server instance
[3/38]: adding default schema
[4/38]: enabling memberof plugin
[5/38]: enabling winsync plugin
[6/38]: configuring replication version plugin
[7/38]: enabling IPA enrollment plugin
[8/38]: enabling ldapi
[9/38]: configuring uniqueness plugin
[10/38]: configuring uuid plugin
[11/38]: configuring modrdn plugin
[12/38]: configuring DNS plugin
[13/38]: enabling entryUSN plugin
[14/38]: configuring lockout plugin
[15/38]: creating indices
[16/38]: enabling referential integrity plugin
[17/38]: configuring ssl for ds instance
[18/38]: configuring certmap.conf
[19/38]: configure autobind for root
[20/38]: configure new location for managed entries
[21/38]: configure dirsrv ccache
[22/38]: enable SASL mapping fallback
[23/38]: restarting directory server
[24/38]: setting up initial replication
Starting replication, please wait until this has completed.
Update in progress, 4 seconds elapsed
Update succeeded[25/38]: updating schema
[26/38]: setting Auto Member configuration
[27/38]: enabling S4U2Proxy delegation
[28/38]: importing CA certificates from LDAP
[29/38]: initializing group membership
[30/38]: adding master entry
[31/38]: initializing domain level
[32/38]: configuring Posix uid/gid generation
[33/38]: adding replication acis
[34/38]: enabling compatibility plugin
[35/38]: activating sidgen plugin
[36/38]: activating extdom plugin
[37/38]: tuning directory server
[38/38]: configuring directory to start on boot
Done configuring directory server (dirsrv).
Configuring certificate server (pki-tomcatd). Estimated time: 3 minutes 30 seconds
[1/24]: creating certificate server user
[2/24]: configuring certificate server instance
[3/24]: stopping certificate server instance to update CS.cfg
[4/24]: backing up CS.cfg
[5/24]: disabling nonces
[6/24]: set up CRL publishing
[7/24]: enable PKIX certificate path discovery and validation
[8/24]: starting certificate server instance
[9/24]: creating RA agent certificate database
[10/24]: importing CA chain to RA certificate database
[11/24]: fixing RA database permissions
[12/24]: setting up signing cert profile
[13/24]: setting audit signing renewal to 2 years
[14/24]: importing RA certificate from PKCS #12 file
[15/24]: authorizing RA to modify profiles
[16/24]: configure certmonger for renewals
[17/24]: configure certificate renewals
[18/24]: configure Server-Cert certificate renewal
[19/24]: Configure HTTP to proxy connections
[20/24]: restarting certificate server
[21/24]: migrating certificate profiles to LDAP
[22/24]: importing IPA certificate profiles
[23/24]: adding default CA ACL
[24/24]: updating IPA configuration
Done configuring certificate server (pki-tomcatd).
Restarting the directory and certificate servers
Configuring Kerberos KDC (krb5kdc). Estimated time: 30 seconds
[1/8]: adding sasl mappings to the directory
[2/8]: configuring KDC
[3/8]: creating a keytab for the directory
[4/8]: creating a keytab for the machine
[5/8]: adding the password extension to the directory
[6/8]: enable GSSAPI for replication
[7/8]: starting the KDC
[8/8]: configuring KDC to start on boot
Done configuring Kerberos KDC (krb5kdc).
Configuring kadmin
[1/2]: starting kadmin
[2/2]: configuring kadmin to start on boot
Done configuring kadmin.
Configuring ipa_memcached
[1/2]: starting ipa_memcached
[2/2]: configuring ipa_memcached to start on boot
Done configuring ipa_memcached.
Configuring the web interface (httpd). Estimated time: 1 minute
[1/18]: setting mod_nss port to 443
[2/18]: setting mod_nss protocol list to TLSv1.0 – TLSv1.2
[3/18]: setting mod_nss password file
[4/18]: enabling mod_nss renegotiate
[5/18]: adding URL rewriting rules
[6/18]: configuring httpd
[7/18]: configure certmonger for renewals
[8/18]: setting up ssl
[9/18]: importing CA certificates from LDAP
[10/18]: publish CA cert
[11/18]: creating a keytab for httpd
[12/18]: clean up any existing httpd ccache
[13/18]: configuring SELinux for httpd
[14/18]: create KDC proxy user
[15/18]: create KDC proxy config
[16/18]: enable KDC proxy
[17/18]: restarting httpd
[18/18]: configuring httpd to start on boot
Done configuring the web interface (httpd).
Configuring ipa-otpd
[1/2]: starting ipa-otpd
[2/2]: configuring ipa-otpd to start on boot
Done configuring ipa-otpd.
Applying LDAP updates
Upgrading IPA:
[1/9]: stopping directory server
[2/9]: saving configuration
[3/9]: disabling listeners
[4/9]: enabling DS global lock
[5/9]: starting directory server
[6/9]: upgrading server
[7/9]: stopping directory server
[8/9]: restoring configuration
[9/9]: starting directory server
Done.
Restarting the directory server
Restarting the KDC
Configuring DNS (named)
[1/9]: generating rndc key file
WARNING: Your system is running out of entropy, you may experience long delays
[2/9]: setting up reverse zone
[3/9]: setting up our own record
[4/9]: adding NS record to the zones
[5/9]: setting up CA record
[6/9]: setting up kerberos principal
[7/9]: setting up named.conf
[8/9]: configuring named to start on boot
[9/9]: changing resolv.conf to point to ourselves
Done configuring DNS (named).
Configuring DNS key synchronization service (ipa-dnskeysyncd)
[1/7]: checking status
[2/7]: setting up bind-dyndb-ldap working directory
[3/7]: setting up kerberos principal
[4/7]: setting up SoftHSM
[5/7]: adding DNSSEC containers
[6/7]: creating replica keys
[7/7]: configuring ipa-dnskeysyncd to start on boot
Done configuring DNS key synchronization service (ipa-dnskeysyncd).
Restarting ipa-dnskeysyncd
Restarting namedGlobal DNS configuration in LDAP server is empty
You can use ‘dnsconfig-mod’ command to set global DNS options that
would override settings in local named.conf filesRestarting the web server
Comprobamos que se haya añadido la replica correctamente:
[root@freeipa02 ~]# ipa-replica-manage list
Directory Manager password:freeipa01.redorbita.com: master
freeipa02.redorbita.com: master
Una vez configurado todo podemos acceder mediante nuestro navegador web https://freeipa01.redorbita.com y administrar nuestro directorio activo desde alli.
En proximos tutoriales entraremos mas a fondo en su configuración.
Un saludo.
Una respuesta a “Instalación y configuración FreeIPA Multi-Master replicación en CentOS 7”